Category: Power Wheelchair
Posted by 2025-12-30 10:12
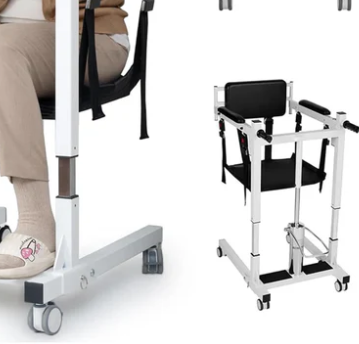
hoyer lift hospital
Hoyer Lift in the Hospital: A Core Transfer Device for Ensuring Patient Safety and Healthcare Efficiency
In the high-intensity and high-risk medical environment of hospitals, the Hoyer Lift has long transcended its role as a "support tool" and become a key infrastructure for safeguarding patient safety, preventing care-related injuries, and improving nursing efficiency. From handling elderly fall victims in the emergency department to transferring critically ill patients in the ICU, from assisting post-operative mobility in rehabilitation wards to helping long-term inpatients with daily toileting needs—the Hoyer Lift is integral to multiple aspects of modern hospital care.
However, hospital scenarios impose far higher requirements on Hoyer Lifts than home environments. hoyer lift hospital Higher frequency of use, more complex patient conditions, stricter infection control standards, and multi-staff collaborative operation models all demand higher standards for equipment performance, operating protocols, and management processes. This article will delve into the application value, usage standards, infection prevention key points, and management strategies of Hoyer Lifts in hospitals, providing references for medical institutions to optimize patient transfer processes.
I. Why Can’t Hospitals Do Without Hoyer Lifts?
1. The Primary Line of Defense for Patient Safety
Patients admitted to hospitals are often in a state of weakness, post-operation, confusion, or under the influence of multiple medications, resulting in extremely low independent transfer ability. Manual lifting can easily lead to:
Patient falls, fractures, and skin tears
Accidental dislodgement of catheters, drainage tubes, and intravenous access
Worsening of existing pressure ulcers or development of new ones
The Hoyer Lift provides stable support through full-body slings, enabling "zero-drag" transfers and significantly reducing the above risks.
2. Protecting the Occupational Health of Healthcare Workers
According to data from the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), over 70% of musculoskeletal injuries among nursing staff result from patient transfer operations. Amid the growing shortage of nurses, reducing physical strain and preventing occupational injuries have become crucial issues in hospital human resource management. The widespread use of Hoyer Lifts is directly linked to staff retention rates and job satisfaction.
3. Improving Care Efficiency and Standardization
A properly deployed Hoyer Lift allows two nurses to complete a bed-to-wheelchair transfer in 3–5 minutes without calling for additional support. Meanwhile, standardized equipment and operating procedures help establish standardized care pathways and reduce human errors.
II. Common Types and Configurations of Hoyer Lifts in Hospitals
Hospitals typically do not rely on a single model but configure different types of lifts based on departmental needs:
Fully Electric Heavy-Duty Models (e.g., Arjo Hoyer Advance, Stryker Prime Mover)
Used in high-dependency patient areas such as ICUs, orthopedics, and neurology departments.
Support quiet operation, high weight capacity (up to over 600 pounds), and floor transfer functionality.
Disinfectable Stainless Steel Sling Systems
Hospitals generally use slings that are quick-drying, antibacterial, and capable of high-temperature cleaning.
Slings are color-coded based on patient isolation levels (e.g., red for contact isolation, green for regular use).
Mobile vs. Fixed Systems
Most wards use mobile Hoyer Lifts for cross-bed use.
Some operating rooms or radiology departments install ceiling-track lift systems to save floor space.
Emergency Rescue Kits
Emergency departments and geriatrics departments keep "floor transfer emergency kits" on hand, hoyer lift hospital which include low-base units and rescue slings for rapid response to fall incidents.
III. Core Usage Standards for Hoyer Lifts in Hospitals
To ensure safety, hospitals typically develop strict Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), including the following key steps:
Two-Person Verification System
Before operation, two nurses jointly confirm: patient identity, medical orders, equipment functionality, and sling type/size.
Infection Control as a Priority
Clean the sling and handle after each use.
Use dedicated slings for isolated patients, and dispose of/clean them according to infection levels after use.
Perform regular terminal disinfection on equipment, especially in multi-drug-resistant organism (MDRO) wards.
Dynamic Risk Assessment
Conduct a quick assessment before transfer: patient consciousness, pain level, number of catheters, weight, and skin condition.
Mechanical lifting is prohibited if contraindications exist, such as unstable fractures or increased intracranial pressure.
Protection of Privacy and Dignity
Draw privacy curtains during operation to minimize body exposure time.
Assist in adjusting clothing and covering the patient with a blanket before and after transfer to reflect humanistic care.
Daily Equipment Status Checks
Check the battery, leg latches, and hook integrity during shift handovers, and record findings in the equipment log.
IV. Common Challenges and Countermeasures
Challenge 1: Insufficient Equipment or Uneven Distribution
Countermeasure: Establish a "centralized Hoyer Lift dispatching system" to improve turnover through QR code booking. Allocate at least 2 units to high-demand departments (e.g., geriatrics).
Challenge 2: Inadequate Nurse Operation Skills
Countermeasure: Incorporate Hoyer Lift operation into new employee orientation training and conduct refresher training every six months. Post visual operation cards next to the equipment.
Challenge 3: Cross-Infection Risk from Slings
Countermeasure: Implement a "one patient, one sling" or "one patient, one disinfection" system. hoyer lift hospital Purchase machine-washable, quick-drying slings to shorten turnover time.
Challenge 4: Slow Response During Night Shifts or Emergencies
Countermeasure: Place "rapid-response Hoyer carts" in corridors or nurse stations, pre-equipped with commonly used slings for immediate deployment.
V. Future Trends: Intelligence and Integration
Leading medical institutions are promoting the intelligent upgrading of Hoyer Lifts:
IoT Connectivity: Equipment usage data is automatically uploaded to nursing systems for staffing and risk early warning.
Voice-Activated Operation: Allow control of lifting/lowering via voice commands when hands are occupied.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Automatically generate task reminders for patient transfers to reduce omissions.
In addition, some newly built hospitals reserve space for Hoyer Lift movement during the architectural design phase, and even integrate ceiling-track systems to achieve "floor-obstacle-free" transfers.
Conclusion: Safe Transfer Is the Cornerstone of High-Quality Healthcare
In hospitals, every transfer from bed to wheelchair is not just a physical movement, but also a safeguard for patient safety, dignity, and rehabilitation progress. hoyer lift hospital As a core tool in this process, the Hoyer Lift’s value has long exceeded the equipment itself—it represents a modern care concept centered on patients, based on evidence, and supported by teamwork.
Investing in and making good use of Hoyer Lifts is not only a form of protection for healthcare workers but also an important measure for hospitals to fulfill their "zero harm" goals and improve overall care quality. In an era of increasingly tight medical resources, leveraging technology to truly serve people is the true essence of a smart hospital.