Category: Power Wheelchair
Posted by 2026-01-05 10:01
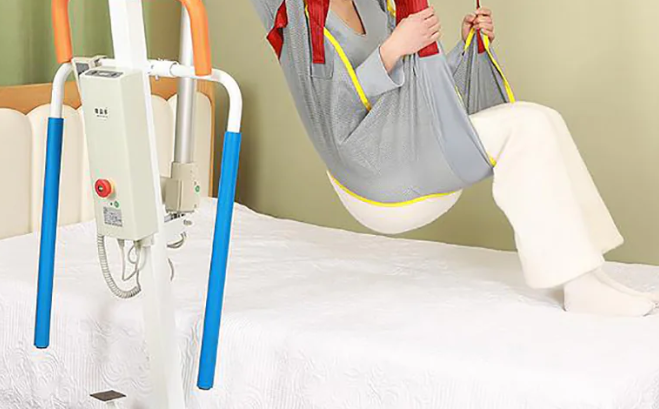
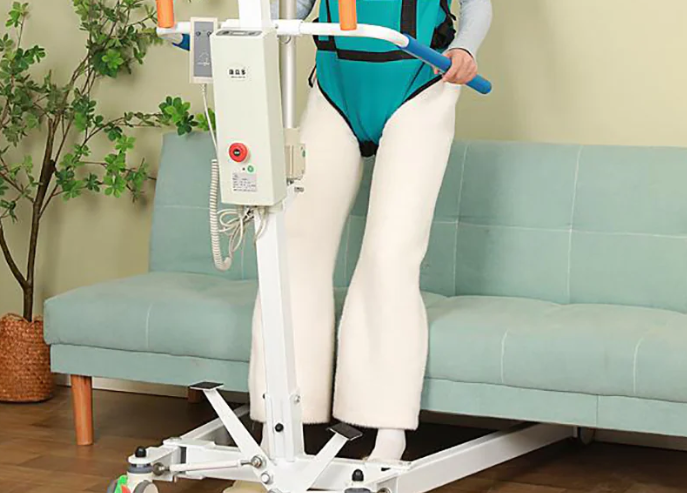
hoyer lift nursing home
Application of Hoyer Lift in Nursing Homes: Standard Practice for Professional Care
In a professional nursing home setting, the Hoyer Lift has evolved into an indispensable tool for high-quality patient care. Its proper use is not only related to patient safety but also directly impacts the quality of care and the operational efficiency of the institution.
Standardized Operation System in Nursing Homes
Equipment Management Specifications
Unified Procurement Standards: Select durable models that meet medical-grade standards.
Regular Maintenance Plans: Establish a preventive maintenance calendar.
Usage Registration System: Record each use in a documented form.
Accessory Inventory Management: Maintain sufficient inventory of slings and consumables.
Staff Training and Certification
Basic Training: New employees must complete 8 hours of hands-on training.
Regular Refresher Training: Conduct skill update training every six months.
Specialized Skills: Training on operation techniques for special cases.
Emergency Handling: Training on standard response procedures for emergency situations.
Multi-department Collaboration Process
Responsibilities of the Nursing Department
Needs Assessment: Evaluate the transfer needs and ability levels of each resident.
Plan Development: Formulate and implement personalized transfer plans.
Daily Operations: Ensure each transfer complies with standard operating procedures.
Effect Evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of equipment use and residents' responses.
Rehabilitation Therapy Department
Functional Training: Conduct functional rehabilitation training in combination with the lift.
Progress Evaluation: Monitor the improvement of residents' functional abilities.
Equipment Adaptation: Adjust equipment usage plans based on rehabilitation progress.
Family Training: Guide family members on the proper use of the equipment.
Management Department
Quality Control: Supervise the quality and safety of equipment use.
Cost Control: Optimize equipment procurement and maintenance costs.
Compliance Audits: hoyer lift nursing home Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Performance Evaluation: Incorporate equipment use into employee performance assessments.
Design of Personalized Care Plans
Classification Based on Assessment
Fully Dependent Type: Residents who require comprehensive assistance.
Partially Participatory Type: Residents with a certain degree of participation ability.
Rehabilitation Training Type: Residents receiving functional training with equipment assistance.
Special Needs Type: Residents with special conditions such as obesity or contractures.
Customized Implementation Plans
Transfer Frequency: Determined based on skin conditions and activity needs.
Participation Level: Encourage residents to participate to the greatest extent possible.
Comfort Optimization: Adjust operation details according to residents' preferences.
Progressive Plan: Modify the usage plan as functional abilities change.
Quality and Safety Monitoring
Safety Indicator System
Fall Prevention: Statistics on transfer-related fall incidents.
Skin Integrity: Assessment of skin conditions after equipment use.
Staff Injuries: Records of transfer-related occupational injuries.
Resident Satisfaction: Questionnaires on residents' equipment usage experience.
Continuous Improvement Mechanism
Incident Reporting: Establish a near-miss and accident reporting system.
Root Cause Analysis: Conduct in-depth analysis of each incident.
Improvement Measures: Develop improvement plans based on analysis results.
Effect Verification: Track the implementation effect of improvement measures.
Special Measures for Infection Control
Cleaning and Disinfection Protocols
Daily Cleaning: Perform basic cleaning immediately after each use.
Deep Disinfection: Conduct thorough disinfection according to a scheduled plan.
Isolation Measures: hoyer lift nursing home Special handling procedures for equipment used by infected residents.
Environmental Management: Infection control requirements for equipment storage areas.
Consumables Management
Personalized Use: Use dedicated slings for individual residents whenever possible.
Cleaning and Disinfection: Establish standardized cleaning and disinfection processes.
Replacement Standards: Clear standards and cycles for consumables replacement.
Inventory Management: Ensure sufficient supply of clean consumables.
Key Care Points for Special Populations
Residents with Dementia
Communication Skills: Use simple and clear operation prompts.
Environment Preparation: Minimize environmental interference and stimulation.
Behavior Management: Professional techniques to handle resistant behaviors.
Emotional Support: Continuous emotional comfort during the operation process.
Obese Residents
Specialized Equipment: Equip with heavy-duty lifts and widened slings.
Operation Techniques: Special body positioning and transfer skills.
Team Collaboration: Develop multi-person collaborative operation plans.
Equipment Maintenance: Increase the maintenance frequency of heavy-duty equipment.
End-of-Life Care
Comfort Priority: Take maximum comfort as the operational guideline.
Family Participation: Encourage family members to participate in the care process.
Environment Creation: Create a quiet and respectful operational environment.
Personalized Care: Respect residents' personal preferences and habits.
Staff Protection and Occupational Health
Ergonomic Optimization
Operation Training: Proper body mechanics and operational postures.
Equipment Adjustment: Adjust equipment settings according to staff height.
Work Organization: Reasonable shift scheduling and work arrangements.
Environment Improvement: Optimize operational space and work processes.
Health Monitoring
Regular Medical Examinations: Monitor staff's musculoskeletal health.
Early Intervention: Early identification and handling of occupational injuries.
Rehabilitation Support: Rehabilitation support for staff with occupational injuries.
Mental Care: Identification and alleviation of work-related stress.
Family Participation and Education
Family Training Programs
Operation Demonstrations: Standard operation demonstrations by professionals.
Hands-on Guidance: Guided practical operation exercises.
Q&A Sessions: Professional answers to family members' questions.
Resource Provision: Sharing of operation guides and video materials.
Communication and Collaboration
Care Meetings: Hold regular meetings to discuss care plans.
Progress Reports: Regularly report residents' progress to family members.
Opinion Collection:hoyer lift nursing home Actively seek family members' opinions and suggestions.
Emotional Support: Provide necessary emotional support for family members.
Facility and Environment Planning
Space Design Standards
Operational Space: Reserve sufficient operational space around each bed.
Storage Space: Plan dedicated equipment storage areas.
Passage Space: Ensure sufficient passage width for equipment movement.
Auxiliary Facilities: Install necessary auxiliary handrails and fixing devices.
Environmental Safety
Lighting Requirements: Ensure adequate lighting in operational areas.
Floor Safety: Select non-slip and flat floor materials.
Emergency Call: Set up a convenient emergency call system.
Monitoring Coverage: Install safety monitoring in key areas.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Direct Costs
Equipment Investment: Procurement costs and depreciation expenses.
Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance and repair expenses.
Consumables Costs: Replacement costs of slings and accessories.
Training Costs: Time and resource investment in staff training.
Indirect Benefits
Reduced Workplace Injuries: Cost savings related to staff occupational injuries.
Quality Improvement: Reputation enhancement brought by improved care quality.
Efficiency Increase: Labor savings from optimized work processes.
Risk Reduction: Potential liability reduction from fewer accidents.
Regulatory Compliance Management
Certification Standards
Regulatory Requirements: Meet the standard requirements of health regulatory authorities.
Certification Standards: Comply with standards of certification bodies such as JCAHO.
Insurance Requirements: Meet the reimbursement requirements of medical insurance.
Local Regulations: Comply with special provisions of local governments.
Documentation Management
Training Records: Maintain complete records of staff training.
Maintenance Logs: Keep detailed records of equipment maintenance history.
Usage Records: Record each instance of equipment use.
Quality Reports: Prepare regular quality assessment and improvement reports.
Technological Innovation and Application
Intelligent Equipment
Electronic Records: Automatic recording system for usage data.
Remote Monitoring: Remote monitoring function for equipment status.
Early Warning System: Early warning system for equipment failures.
Data Analysis: Intelligent analysis function for usage data.
Future Trends
IoT Integration: Intelligent linkage between devices.
Artificial Intelligence: Intelligent usage recommendations and early warnings.
Virtual Training: VR-based operation training systems.
Mobile Applications: Convenient equipment management applications.
Conclusion
In a professional nursing home environment, the Hoyer Lift has gone beyond the role of a simple transfer tool and become a core component of the high-quality care system. hoyer lift nursing home Through standardized operation processes, personalized care plans, strict quality control, and continuous skill training, nursing homes can provide residents with safe, comfortable, and dignified care services. In this process, the equipment is not only a tool for care but also a reflection of the concept of professional care and a concrete practice of the nursing home's commitment to residents.