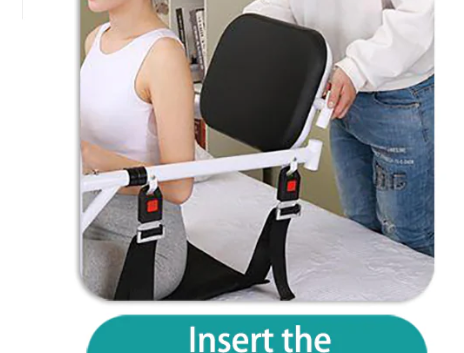
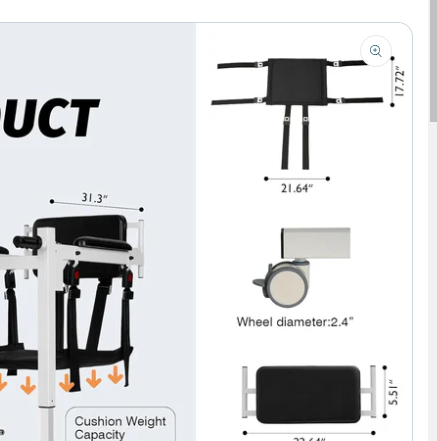
Category: Electric Transfer Chair
Posted by 2026-01-03 10:01
hoyer lift medicare
The Complete Guide to Hoyer Lifts and Health Insurance: Maximize Your Benefit Coverage
Understanding Medicare’s coverage policy for Hoyer Lifts is crucial for patients in need of this vital medical equipment. hoyer lift medicare A proper grasp of the policy and application process can help you significantly reduce financial burdens while accessing the necessary care support.
Medicare Part B Coverage Basics
Eligibility Criteria
Medical Necessity: A doctor must certify that the equipment is medically necessary for in-home care.
In-Home Use: The equipment must be primarily used in a home setting.
Functional Limitations: The patient must have significant limitations in transfer ability.
Expected Usage Period: Long-term use is required (typically more than 6 months).
Coverage Scope
Equipment Rental: Generally covers rental costs for 13 months.
Subsequent Ownership: Patients gain ownership of the equipment after the rental period ends.
Related Accessories: Necessary slings and basic accessories.
Maintenance Services: Essential repair and maintenance services.
Detailed Application Process
Step 1: Medical Assessment
Physician Evaluation: Complete a detailed functional assessment.
Documentation Preparation: Include medical history, diagnosis, and proof of functional limitations.
Necessity Certification: Clearly explain why a lift is essential.
Treatment Plan: Define the role of the equipment in the overall treatment plan.
Step 2: Supplier Selection
Participating Suppliers: Choose a durable medical equipment (DME) supplier that participates in Medicare.
Qualification Verification: Confirm the supplier’s Medicare enrollment status.
Price Negotiation: Understand Medicare’s approved price range.
Service Evaluation: Compare the quality of services offered by different suppliers.
Step 3: Document Submission
Prescription Requirement: A detailed prescription issued by a physician.
Assessment Report: Complete documentation proving medical necessity.
Application Forms: Fill out the application forms required by Medicare.
Supporting Documents: All relevant medical records.
Cost-Sharing Analysis
Cost-Sharing Structure
Annual Deductible: Must first pay the Part B annual deductible ($240 in 2024).
Coinsurance: Pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount.
Excess Charges: Participating suppliers cannot charge more than 15% above the Medicare-approved amount.
Accessory Costs: Cost-sharing ratio for additional accessories.
Cost-Control Strategies
Supplier Selection: Choose a supplier that accepts assignment (agrees to Medicare’s approved price).
Price Comparison: hoyer lift medicare Compare charges from different suppliers.
Accessory Management: Select only necessary accessories.
Timing Planning: Consider applying after meeting the annual deductible.
Key Points for Proving Medical Necessity
Functional Documentation Requirements
Transfer Ability Assessment: Detailed description of limitations in independent transfer.
Fall Risk: Provide specific fall risk assessment results.
Care Needs: Explain the inadequacy of current care arrangements.
Alternative Solutions: Analyze why other transfer methods are not feasible.
Clinical Supporting Evidence
Diagnostic Proof: Relevant medical diagnosis documents.
Treatment History: Evaluation of the effectiveness of previous treatments and interventions.
Prognostic Judgment: Expected duration and effectiveness of equipment use.
Safety Considerations: Risks associated with not using the equipment.
Common Denial Reasons and Responses
Denial Analysis
Incomplete Documentation: Insufficient proof of medical necessity.
Supplier Issues: Problems with the supplier’s qualifications or documentation.
Technical Errors: Incorrect or incomplete application form filling.
Policy Misunderstanding: Misinterpretation of coverage terms.
Appeal Strategies
Timely Response: Submit an appeal within the specified timeframe.
Supplementary Evidence: Provide additional medical evidence.
Professional Assistance: Seek help from patient advocacy organizations.
Progressive Appeals: Utilize the multi-level appeal process.
Handling Special Cases
Progressive Diseases
Long-Term Needs: Prove the long-term necessity of the equipment.
Functional Changes: Regularly update assessment documents.
Equipment Upgrades: Apply for equipment upgrades if the condition worsens.
Periodic Re-evaluations: Comply with periodic re-evaluations may be required by Medicare.
Multiple Comorbidities
Comprehensive Impact: Explain how multiple diseases collectively affect function.
Care Complexity: Highlight the complexity of care arrangements.
Risk Accumulation: Cumulative effects of multiple risk factors.
Quality of Life: The equipment’s impact on overall quality of life.
Coordinating Supplementary Insurance
Medigap Policies
Cost Coverage: Help cover out-of-pocket expenses.
Application Assistance: Provide additional support for the application process.
Appeal Support: Offer professional help in case of claim denials.
Network Access: Access to a broader network of suppliers.
Medicare Advantage Plans
Plan Differences: Variations in coverage among different plans.
Network Restrictions: Specific supplier network requirements.
Prior Authorization: Additional authorization processes that may be required.
Coordination Rules: hoyer lift medicare Rules for coordinating with Original Medicare.
Annual Updates and Changes
Policy Monitoring
Rate Changes: Annual changes to premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Coverage Updates: Revisions to coverage scope and conditions.
Process Adjustments: Changes to application and approval procedures.
Supplier Changes: Updates to the list of participating suppliers.
Adaptation Strategies
Stay Informed: Monitor Medicare’s annual announcements.
Professional Consultation: Regularly consult with Medicare experts.
Plan Review: Annual review and adjustment of insurance plans.
Budget Planning: Adjust cost budgets based on policy changes.
State-Level Supplementary Programs
Medicaid Coordination
Dual Eligibility: Coordinate benefits for individuals eligible for both Medicare and Medicaid.
Cost Waivers: Medicaid may cover out-of-pocket expenses.
Application Assistance: Additional application support from state programs.
Local Differences: Understand variations in policies across states.
State-Specific Programs
Special Programs: State-specific programs for individuals with special needs.
Financial Assistance: Income-based additional financial aid.
Service Coordination: Coordination services for care management.
Local Resources: Access to local supplementary resources and support.
Long-Term Planning Recommendations
Lifecycle Management
Equipment Lifespan: Consider the expected lifespan of the equipment.
Upgrade Planning: Plan for upgrades based on technological advancements and changing needs.
Maintenance Budget: Budget for long-term maintenance and accessory replacement.
Alternative Arrangements: Develop emergency plans for equipment failures.
Care Continuity
Caregiver Training: Ensure ongoing training and support for caregivers.
Environment Adaptation: hoyer lift medicare Adapt the living environment to accommodate the equipment.
Transition Planning: Ensure smooth transitions between different care settings.
Quality Maintenance: Maintain and improve the quality of ongoing care.