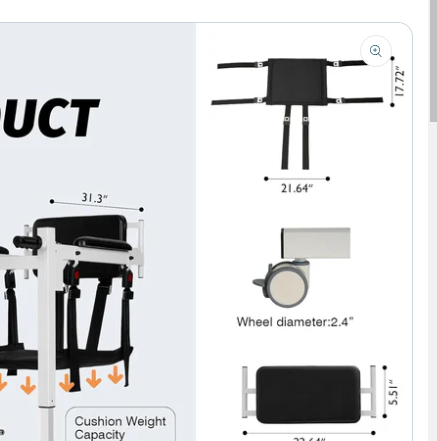
Category: Electric Transfer Chair
Posted by 2025-12-30 11:12
hoyer lift hydraulic pump
In-Depth Analysis of Hoyer Lift Hydraulic Pump Systems: The Science and Art of the Power Core
The hydraulic pump is the power source of a manual Hoyer Lift. This precision mechanical system converts simple manual operations into smooth and reliable lifting force. hoyer lift hydraulic pump Gaining a deep understanding of the hydraulic pump’s working principles and maintenance requirements is key to ensuring the long-term and reliable operation of the equipment.
Working Principles of the Hydraulic Pump System
Basic Mechanical Design
Application of Pascal’s Law: Transmitting and amplifying pressure through incompressible fluids.
Optimization of Lever Principle: Precise calculation of handle length and pump body diameter.
One-Way Valve System: Ensuring the one-way flow of hydraulic oil to maintain the lifted state.
Pressure Balance Mechanism: Automatically compensating for pressure changes within the system.
Composition of Core Components
Pump Chamber: A precision-machined space for containing hydraulic oil.
Main Piston: Features a specially treated surface to ensure smooth movement and sealing performance.
Oil Inlet/Outlet Valves: A one-way flow system controlled by precision springs.
Handle Mechanism: An ergonomic lever transmission system.
Sealing Assemblies: Multi-layer seals to ensure zero-leakage performance.
Analysis of Operational Characteristics
Pump Pressure Cycle Process
Suction Phase: Lifting the handle creates negative pressure to draw in hydraulic oil.
Compression Phase: hoyer lift hydraulic pump Pressing down the handle forces oil into the main hydraulic cylinder.
Locking Phase: The one-way valve automatically closes to maintain pressure.
Cycle Repetition: Continuous operation achieves smooth lifting.
Performance Parameter Indicators
Single Pump Pressure Stroke: Typically lifts 1–2 centimeters per stroke.
Operational Force Requirement: Optimized lever ratio ensures easy operation.
Flow Control: Precise oil volume control enables fine-tuning capabilities.
Pressure Limit: Built-in safety valve prevents system overload.
Professional Maintenance Guide
Daily Inspection Protocol
External Inspection: Check for oil stains or damage on the pump body.
Function Test: Inspect operational smoothness and abnormal noises.
Connection Check: Confirm all connecting parts are secure and reliable.
Seal Evaluation: Inspect visible seals for signs of aging.
Preventive Maintenance Plan
Weekly: Clean the exterior and check operational feel.
Monthly: Conduct a detailed inspection of sealing performance and test load-bearing capacity.
Quarterly: Professionally test the function of internal valves.
Annually: Perform a full disassembly inspection and replace worn parts.
Hydraulic Oil Management Specifications
Oil Specifications: Strictly follow the oil type recommended by the manufacturer.
Oil Level Monitoring: Regularly check the oil level via the sight glass.
Oil Quality Evaluation: Inspect the oil’s color, viscosity, and cleanliness.
Replacement Cycle: Typically every 2–3 years, or determined by usage frequency.
Expert Guide to Troubleshooting
Analysis of Common Issues
Weak Lifting: Insufficient oil level, aged oil, or air entrainment.
Automatic Lowering: Worn seals or valve failure.
Heavy Operation: Excessively viscous oil or internal contamination.
Abnormal Noises: Air entry or worn mechanical components.
Systematic Troubleshooting Methods
Symptom Analysis: Accurately describe the problem’s manifestations and occurrence conditions.
External Inspection: Check the integrity of visible components.
Function Test: Conduct diagnostic tests under safe conditions.
Root Cause Analysis: Identify the underlying cause of the problem.
On-Site Emergency Measures
Immediately stop using the faulty equipment.
Record detailed manifestations of the problem.
Implement necessary safety precautions.
Contact professional maintenance services.
Performance Optimization Strategies
Improvement of Operational Skills
Rhythm Control: Maintain a smooth and continuous pump pressure rhythm.
Force Mastery: Avoid excessive force that may damage the sealing system.
Position Optimization: Choose the optimal operating stance and posture.
Preventive Measures: Fully inspect the system status before operation.
Environmental Adaptability
Temperature Impact: Understand the characteristics of hydraulic oil under different temperatures.
Storage Conditions: Avoid extreme temperature and humidity environments.
Cleanliness Requirements: Keep the system free from contamination and corrosion.
Usage Frequency: Adjust the maintenance plan based on operation intensity.
Safety Engineering Features
Multi-Protection Design
Overpressure Protection Valve: Automatically releases pressure exceeding the design limit.
Mechanical Limit: Prevents the piston from exceeding its stroke range.
Structural Strength: Designed with a sufficient safety factor.
Emergency Release: A reliable pressure release system for fault scenarios.
Safety Specifications for Use
Strictly follow the rated operational force requirements.
Prohibit the use of non-original accessories and oil.
Conduct regular professional safety inspections.
Establish a comprehensive operational training system.
Development of Technological Innovations
Trends in Modern Improvements
Material Science: New composite materials enhance durability.
Sealing Technology: Long-life sealing materials extend maintenance intervals.
Ergonomics: Optimize operational comfort and efficiency.
Intelligent Monitoring: Integrate functions for monitoring usage status.
User Experience Optimization
Operational Feedback: Clear tactile and audio feedback.
Maintenance Indicators: Intelligent reminders for maintenance needs and intervals.
Adaptive Design: Ergonomics adapted to different operators.
Quick Maintenance: Modular design simplifies maintenance processes.
Professional Technical Comparison
Advantages of Hydraulic Pump Systems
Precise fine-tuning control capabilities.
Smooth force transmission characteristics.
Reliable pressure retention performance.
Lower technical requirements for maintenance.
Application Scenario Analysis
Long-Term Care Facilities: Reliable performance for daily use.
Home Care Environments: Simple maintenance requirements.
Budget-Sensitive Projects: Excellent cost-effectiveness ratio.
Technical Preference Selection: High trust in mature mechanical principles.
Professional Purchasing Guide
Quality Evaluation Standards
Pump body machining precision and surface treatment quality.
Design and material grade of the sealing system.
Smoothness and consistency of operational feel.
The manufacturer’s technical capabilities and after-sales service.
Matching Usage Requirements
Evaluate the expected frequency and intensity of use.
Consider the physical limitations of operators.
Analyze the temperature range of the usage environment.
Determine the expected service life of the equipment.
Conclusion
The Hoyer Lift hydraulic pump system represents the perfect integration of mechanical precision and practical reliability. hoyer lift hydraulic pump This seemingly simple yet technically profound system converts human effort into smooth and reliable lifting force through exquisite engineering design. Gaining a deep understanding of its working principles, mastering correct operational skills, and implementing strict maintenance procedures are the foundation for ensuring the long-term and reliable service of this important equipment. During the selection and use process, remember: a high-quality hydraulic pump system requires professional operational coordination. Only the perfect combination of the two can provide the safest and smoothest guarantee for every transfer.