Category: Patient Lifts
Posted by 2025-12-26 13:12
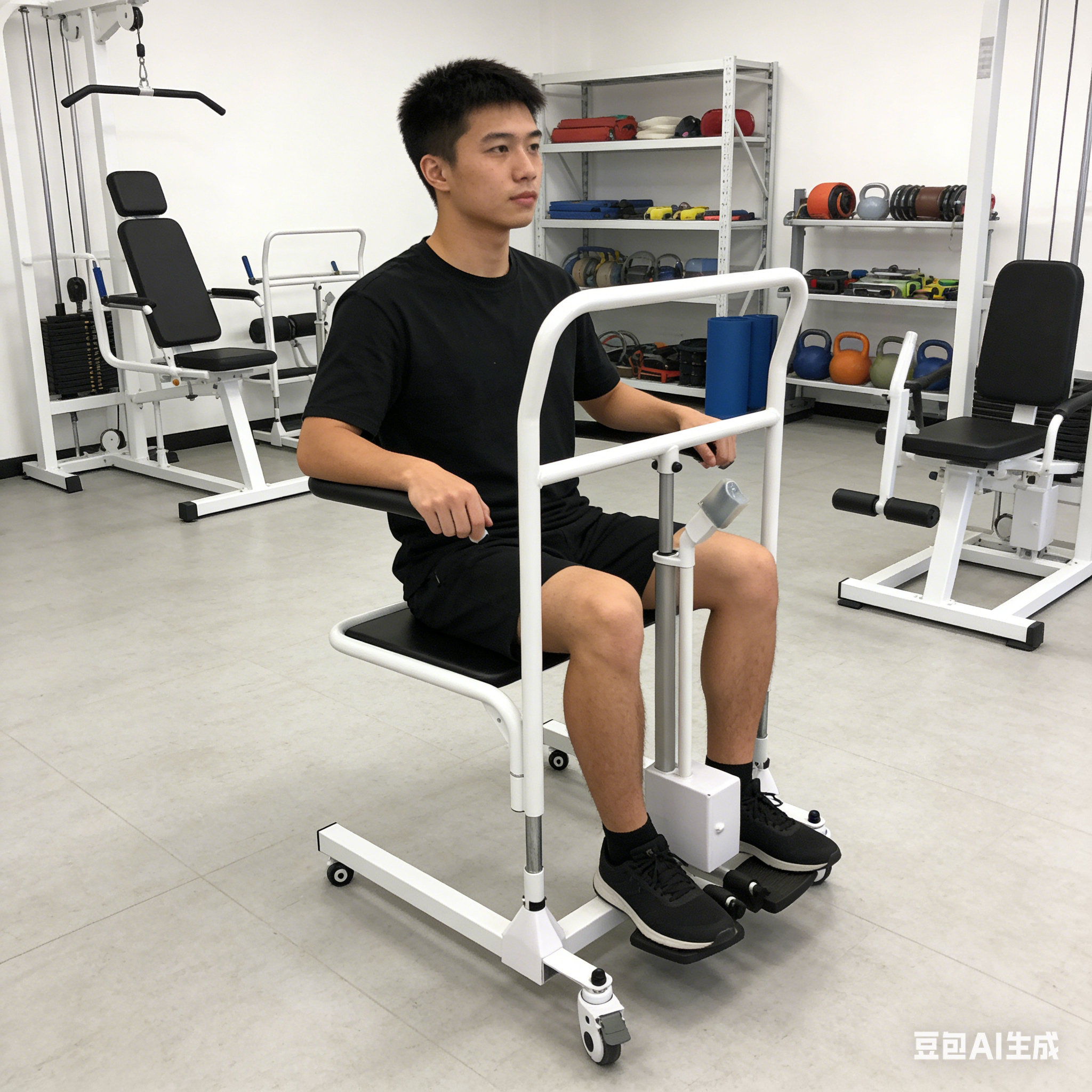
hoyer lift floor
I. Why Standard Hoyer Lifts Struggle with Floor Transfers?
Although Hoyer lifts are widely used for bed-to-chair transfers, their standard design is not suitable for lifting users directly from the floor. The main reasons include:
Base Height Limitation
Most mobile Hoyer lifts have a leg-to-floor height of 10–15 cm, which prevents the base from being placed close to the floor. This makes it difficult to thread the sling under a user lying flat.
Too High Lowest Point of the Boom
Even when the hydraulic system can be lowered, the hook or sling attachment point usually cannot go below 8–10 cm, making "zero-height lifting" impossible.
Difficulty in Threading the Sling
Standard full-body slings need to be slid under the user's back. However, the narrow space on the floor and high friction make it easy to cause skin damage if forced to drag the sling.
⚠️ If standard equipment is used forcefully, caregivers often have to manually drag the user onto an elevated object first. This process is highly likely to cause secondary injuries.
II. Types of Hoyer Lifts Optimized for Floor Scenarios
1. Low-Base or Removable Leg Models
Core Design: The legs can be folded inward or completely removed, allowing the main unit's base to be almost flush with the floor.
Minimum Boom Height: Can be lowered to within 5 cm.
Representative Models:
Arjo Hoyer Advance (supports "Floor Mode")
Invacare Lifestand Pro
Stryker Prime Mover
Chinese brands such as KDB-Floor series, Yearstar Low-Profile Lift
2. Floor Slings / Rescue Slings
Even with a standard main unit, using a dedicated sling can significantly improve the feasibility of floor transfers:
Front-opening design: Can be worn without turning the user over.
Bottom sliding rails or lifting straps: Facilitate dragging from the floor.
Lightweight and wear-resistant material: Reduces resistance when threading.
Handle-equipped version: Supports multi-person collaboration to initially drag the user to a hard-surface area.
✅ Common Types: Universal Floor Sling, Hygiene Floor Sling (with an opening for toileting), Emergency Rescue Sling
3. Slide Sheet + Standard Lift Method
First, use a low-friction slide sheet to move the user from the carpet/soft cushion to the edge of the hard floor.
Then, operate the standard Hoyer lift from the side.
Suitable for families with limited budgets but in need of emergency floor transfer solutions.
III. Standard Operating Procedure (Safety Version)
Prerequisite: Confirm that the user has no spinal, pelvic, or lower limb fractures. hoyer lift floor If in doubt, call for emergency assistance immediately.
On-Site Assessment
Clear surrounding obstacles.
Check if the floor is dry and level.
Equipment Preparation
Install the floor-specific sling.
Remove or fold the Hoyer lift legs (if supported).
Threading the Sling
Gently assist the user to lie on their side.
Slide the sling under the user's back and adjust the leg loops.
Fasten all connection points to ensure no twisting.
Slow Lifting
Start the lift and raise the user steadily at the lowest speed.
Observe the user's facial expression and reactions.
Completing the Transfer
Rotate the lift to the target position (wheelchair/bed).
Lower the user slowly and assist them to sit or lie down properly.
IV. Key Purchasing Recommendations
Consideration Item Recommended Solution
Equipment Type Prioritize models clearly labeled "Floor Transfer Capable".
Sling Compatibility Confirm that the main unit supports third-party floor slings (e.g., Arjo, Liko standards).
Space Adaptability Measure door width and corridor corners to ensure the low-base model can enter.
Power Supply & Portability For home use, 220V electric models are recommended; for travel, hoyer lift floor a portable lift + slide sheet combination is suitable.
Training Support Choose suppliers that provide video tutorials or on-site training.
V. Practical Application Value
Reducing Occupational Injuries: Caregivers do not need to bend over to lift, reducing the risk of lower back injuries by over 70%.
Improving Response Speed: Professional institutions can achieve "safe transfer within 10 minutes after a fall".
Preserving Dignity: Avoids psychological trauma caused by prolonged stays on the floor.
Preventing Complications: Reduces secondary risks such as pressure sores, hypothermia, and urinary retention.