Category: Electric Transfer Chair
Posted by 2025-12-26 11:12
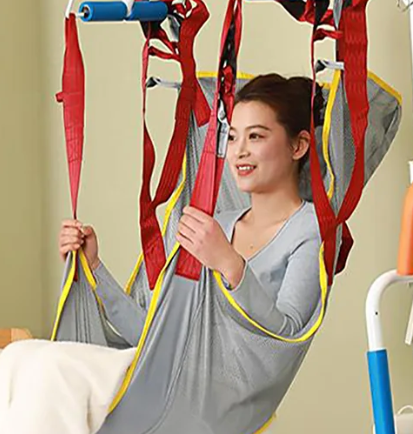
hoyer lift fabric
Core Performance Indicators of Sling Fabrics
Strength and Durability
Tensile Strength: Must withstand more than 5 times the user's body weight.
Abrasion Resistance: Standard requires passing 50,000 friction tests.
Seam Strength: The strength at the stitching should not be less than 80% of the fabric itself.
Safety Performance
Flame Retardancy: Complies with fire safety standards for medical equipment.
Anti-static Property: Prevents discomfort caused by static accumulation.
Color Fastness: Ensures dyes do not fade due to washing or sweat.
Comfort Performance
Breathability: Allows air circulation to reduce stuffiness.
Softness: Comfortable touch when in contact with the skin.
Elasticity: Moderate stretchability under load.
In-depth Analysis of Mainstream Fabric Types
1. Nylon Fabric
Characteristics: High strength, excellent abrasion resistance, relatively lightweight.
Advantages: Long service life, outstanding load-bearing performance.
Disadvantages: Average breathability, obvious static electricity.
Applicable Scenarios: High-frequency daily use, users with heavier body weight.
2. Polyester Fiber
Characteristics: Good dimensional stability, strong wrinkle resistance.
Advantages: Easy to clean and dry, maintains shape well.
Disadvantages: Poor softness, may generate static electricity.
Applicable Scenarios: Medical environments requiring frequent cleaning.
3. Mesh Fabric
Characteristics: High breathability, excellent quick-drying performance.
Advantages: Excellent ventilation effect, lightest weight.
Disadvantages: Relatively low strength, limited abrasion resistance.
Applicable Scenarios: Toileting and bathing purposes, hoyer lift fabric use in hot environments.
4. Blended Fabric
Characteristics: Combines the advantages of multiple fibers.
Advantages: Balances strength, comfort, and durability.
Disadvantages: Higher cost, complex maintenance requirements.
Applicable Scenarios: High-end models, users with special needs.
Professional Fabric Treatment Technologies
Antibacterial Treatment
Silver Ion Technology: Provides long-lasting antibacterial protection.
Nanocoating: Prevents bacteria from growing on the fiber surface.
Hygienic Finishing: Inhibits the growth of fungi and mildew.
Reinforcement Treatment
Tear-Resistant Weaving: Adopts a grid-like reinforced structure.
Edge Reinforcement: Special reinforcement for high-wear areas.
UV Stabilizer: Prevents aging caused by sunlight exposure.
Comfort Treatment
Softener Finishing: Improves the fabric's hand feel.
Moisture-Wicking: Quickly diverts moisture away from the skin surface.
Temperature Regulation: Phase-change materials provide intelligent temperature control.
Fabric Selection Guide
Based on Usage Environment
Medical Institutions: Prioritize durable and easy-to-sterilize fabrics.
Home Care: Focus on comfort and ease of maintenance.
Outdoor Use: Consider UV resistance and hydrolysis stability.
Based on User Conditions
Sensitive Skin: Choose fabrics with high softness and certified hypoallergenic properties.
Incontinent Patients: Need quick-drying and impermeable materials.
Obese Patients: Require higher strength and abrasion resistance.
Based on Usage Frequency
High-Frequency Daily Use: Durability is the top priority.
Occasional Use: Focus on comfort and cost-effectiveness.
Scientific Maintenance and Care
Cleaning Specifications
Water Temperature Control: Usually not exceeding 60°C.
Detergent Selection: Neutral detergent, avoid bleach.
Drying Method: Air-dry naturally or tumble dry at low temperature.
Sterilization Guidelines
Chemical Sterilization: Use approved medical-grade disinfectants.
Thermal Sterilization: Perform within the allowable temperature range.
UV Sterilization: Use as an auxiliary sterilization method.
Storage Requirements
Environmental Conditions: Avoid direct sunlight, keep dry.
Folding Method: Avoid long-term folding at the same position.
Regular Inspection: Unfold and check the fabric condition monthly.
Safety Testing Standards
Visual Inspection Key Points
Color Change: May indicate fabric aging.
Abrasion Signs: Pilled, thinned, or shiny areas.
Damage Check: Tears, holes, or worn spots.
Hand Feel Inspection
Softness Change: Abnormal hardening may indicate aging.
Thickness Uniformity: Check for thinned areas.
Elasticity Test: Ensure proper rebound performance.
Functional Testing
Load-Bearing Test: Conduct regular safe load tests.
Seam Inspection: Ensure all stitches are intact.
Hook Area: Check the integrity of reinforced parts.
Cutting-Edge Innovative Fabric Technologies
Smart Fabrics
Pressure Sensing: Real-time monitoring of pressure distribution.
Temperature Monitoring: Built-in temperature sensors.
Humidity Detection: Signals indicating the need for replacement.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Recycled Fibers: Made from recycled materials.
Biodegradable: Environmentally friendly disposal solutions.
Energy-Saving Production: Reduce energy consumption during production.
Enhanced Functions
Self-Cleaning Coating: Reduce cleaning frequency.
Shape Memory: Automatically adapts to the user's body shape.
Antibacterial Upgrade: Longer-lasting hygiene protection.
Conclusion
Sling fabric is a seemingly ordinary but crucial component of the Hoyer Lift system. Choosing the right fabric can significantly improve the user experience, extend the equipment's service life, hoyer lift fabric and most importantly, ensure safety in use. Understanding fabric science and establishing a system of regular inspection and replacement are essential knowledge for every responsible user and caregiver. hoyer lift fabric Remember, never compromise on quality and safety when it comes to slings—components that are in direct contact with the body. Investing in high-quality fabrics is an investment in long-term comfort and peace of mind.