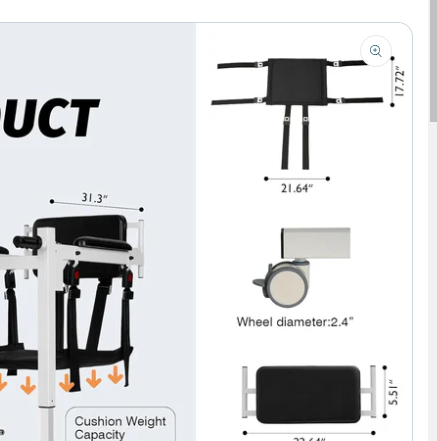
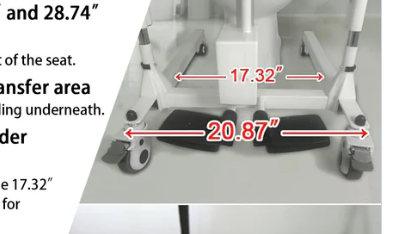
Category: Electric Transfer Chair
Posted by 2025-12-30 11:12
hoyer lift how many people
Hoyer Lift Operator Staffing Guide: A Comprehensive Plan from Solo Operation to Team Collaboration
The number of staff assigned to operate a Hoyer Lift directly impacts the safety and efficiency of the transfer process. hoyer lift how many people Proper team configuration not only ensures the user’s safety but also protects caregivers from occupational injuries. This guide will detailedly analyze staffing requirements across different scenarios to help you establish an optimized operation team.
Core Principles of Staffing Configuration
Safety-First Principle
The user’s safety is the top priority in all situations.
Caregivers’ safety is equally important; avoid assigning solo staff to high-risk operations.
Staffing should be based on risk assessment results.
It is better to overstaff than to take unnecessary risks.
Competence-Matching Principle
Operators must have relevant training and certification.
Physical capability should match the task requirements.
Experience levels should be reasonably distributed within the team.
The ability to respond to emergencies is an essential qualification.
Staffing Standards for Different Scenarios
Standard Bed-to-Wheelchair Transfer (1-Person Configuration)
Applicable Conditions:
The user can cooperate with the operation and has clear cognition.
The user’s weight is within 60% of the equipment’s load capacity.
The space is spacious with no obstacles along the transfer path.
The caregiver has rich experience and sufficient physical strength.
Operation Process:
The solo operator completes all preparation work.
Independently operates the lift to finish the transfer.
Simultaneously takes charge of communicating with the user and providing reassurance.
Conducts post-transfer equipment reset and environment tidying.
Complex Transfer Scenarios (2-Person Team)
Mandatory Conditions:
The user’s weight is close to the equipment’s maximum load capacity.
The user has cognitive impairment or communication difficulties.
The transfer path is complex or obstructed.
The user has special medical needs.
Division of Roles:
Primary Operator: Responsible for equipment control and main operational steps.
Assistant: Stabilizes the user, monitors the environment, and assists with communication.
Special Medical Conditions (3+ Person Team)
Applicable Situations:
Transfer of critically ill patients or post-surgical patients.
Transfer of extremely obese users (weighing over 150 kg).
Complex rescue operations for users who have fallen to the floor.
Transfer of users with severe behavioral issues.
Team Configuration:
Equipment Operation Specialist
Medical Monitoring Staff
User Stabilization Specialist
On-Site Command Coordinator
Professional Guide for Solo Operation
Qualification Requirements
Completion of at least 40 hours of professional training.
Passing of practical operation assessment.
Mastery of emergency response procedures.
Good physical strength and stamina.
Key Safety Operation Points
Conduct a strict pre-operation risk assessment.
Ensure all safety devices are functioning properly.
Establish an emergency assistance mechanism.
Be aware of personal operational limits and avoid overexertion.
Efficiency Optimization Tips
Pre-plan the optimal transfer path.
Prepare all necessary auxiliary equipment in advance.
Establish standardized operation procedures.
Maintain proper body mechanics posture.
Best Practices for Team Collaboration
Clear Role Division
Commander: Responsible for overall coordination and decision-making.
Equipment Operator: Focuses on lift control.
User Caregiver: Monitors the user’s condition and comfort level.
Environment Observer: hoyer lift how many people Ensures path safety and equipment stability.
Communication Protocol
Use clear standard terminology.
Establish a confirmation response mechanism.
Develop clear hand signals.
Pre-arrange emergency codes.
Key Focus Areas for Team Training
Conduct regular team coordination drills.
Provide cross-training to enhance multi-skill capabilities.
Build team rapport and trust.
Carry out post-operation reviews and improvements.
Staffing for Special Situations
Care for Obese Users
Basic Configuration: At least 2 physically strong operators.
Ideal Configuration: A 3-person team including a dedicated equipment manager.
Equipment Requirements: Heavy-duty lift and widened sling.
Space Requirements: Larger operation and turning space.
Care for Patients with Cognitive Impairment
Staff Requirements: Operators with experience in behavior management.
Team Configuration: 2 people (one focusing on equipment, the other on user reassurance).
Scheduling: Allocate sufficient time to avoid rushing.
Environment Preparation: Minimize distracting factors.
Care for Patients in Rehabilitation Period
Team Composition: Including a physical therapist or occupational therapist.
Operation Goal: Balance safety and functional training.
Staff Skills: Understanding of rehabilitation principles and progress management.
Documentation Requirements: Detailed records of functional improvement.
Training and Certification System
Basic Training Content
Knowledge of equipment principles and structure.
Training on standard operation procedures.
Safety standards and risk assessment.
Emergency response drills.hoyer lift how many people
Team Collaboration Training
Clarification of role division and responsibilities.
Training on effective communication skills.
Establishment of team decision-making processes.
Learning of conflict resolution mechanisms.
Continuing Education Requirements
Annual retraining and skill updates.
Training on new equipment and technologies.
Case analysis and experience sharing.
Learning of updated safety standards.
Staff Safety Management
Occupational Health Protection
Train staff on proper body mechanics.
Provide necessary personal protective equipment.
Establish a reasonable work rotation system.
Conduct regular health check-ups.
Psychological Support System
Provide stress management training.
Establish a colleague support network.
Offer professional psychological counseling services.
Recognize and reward outstanding performance.
Emergency Preparation Plan
Clear emergency response procedures.
Regular emergency drills.
Equip necessary first-aid supplies.
Establish a rapid response mechanism.
Collaboration Between Technology and Staff
Equipment Auxiliary Functions
Electric models reduce physical exertion requirements.
Smart sensors provide operational assistance.
Emergency stop devices enhance safety.
Weight display helps with risk assessment.
Information Management
Record staffing configuration for each operation.
Analyze accident and near-miss data.
Provide recommendations for team configuration optimization.
Offer personalized training plans.
Conclusion
Staffing configuration for Hoyer Lift operation is a science that balances safety, efficiency, and humanization. hoyer lift how many people From skilled solo operations to well-coordinated team collaboration, every configuration plan should center on the user’s safety and dignity. Remember, the best team configuration is not a fixed formula but an intelligent choice based on specific needs and conditions. Through professional training, clear role division, and continuous improvement, we can provide the most appropriate staffing support for every transfer, making care work not only safe and reliable but also full of human warmth.